 It is a difficult task to choose a birth control option for women aged 40-49 due to the peculiarities of this age period associated with:
It is a difficult task to choose a birth control option for women aged 40-49 due to the peculiarities of this age period associated with:
- the inevitable processes of gradual extinction of ovarian function;
- the presence of several gynecological and extragenital diseases;
- the appearance of vegetative-vascular;
- other early symptoms of menopause.
When choosing a birth control in this age period, the question arises of how to avoid the effect on metabolic processes that have undergone on the background of the high sensitivity of the female body to exogenous influences. Prevention and treatment of the initial symptoms of the climacteric syndrome and, if possible, slowing down the aging process are among the main tasks of contraception at this age.
Hormonal implants
Hormonal implants contain pure progestogen. It is a safe group of birth control for women in the older age group. When used, there are no side effects of estrogen. The advantages of this type of contraceptive are the release of low doses of hormones, the dosing accuracy, the absence of daily fluctuations in the level of hormones, the need for daily self-control, and primary passage through the gastrointestinal tract.
An implant looks like a small, flexible, thin device that is inserted under the skin of the inner surface of the shoulder. It provides continuous contraceptive effect for three years. The hormone, a part of this implant, reliably suppresses ovulation, but at the same time, does not suppress the production of its endogenous estrogens, that is, it does not cause a climacteric effect.
Implants are often chosen by women who are not sure that they can take birth control pills every day correctly at the same time.
The most common side effect of hormonal implants is irregular menstruation. In clinical trials, one in ten women refused to use birth control implants due to a menstruation disorder. During the entire period of its use, menstruation can be irregular and unpredictable. The intervals between menstruation can vary. During the cycle, spotting bleeding can be troublesome. In the course of clinical studies, side effects were also recorded:
- headache;
- vaginitis;
- weight gain;
- skin problems;
- pain in the mammary glands;
- mood swings;
- nervousness;
- depression;
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- pain at the injection site.
Intrauterine devices
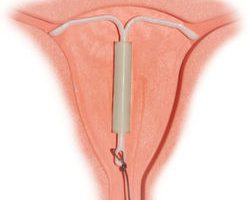
The issue of using intrauterine devices in women over 40 years of age is of particular interest. The use of IUD of the 2nd generation can have a negative side in the form of the bleeding, the likelihood of which already increases in perimenopause. This problem can be solved by using 3rd generation birth control intrauterine devices. The hormone reduces the volume of blood loss. Also, when a woman is taking estrogen preparations as replacement therapy, it can protect against the development of hyperplastic processes. There is still a chance of pregnancy even in menopausal women. In this case, IUDs have high contraceptive activity. In a survey conducted among women over 40 years old, it was found that over 90% of them preferred an intrauterine device as a method of birth control.
It is important to note that, unlike oral contraceptives, hormonal IUDs do not harm the hemostatic system, lipid metabolism, body weight, and blood pressure indicators. However, there is a possibility of an effect on glucose tolerance. Therefore, the use of intrauterine contraceptives in patients with diabetes mellitus should be carried out with caution, and constant monitoring of blood glucose levels is necessary.
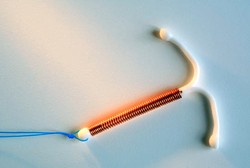
Copper T IUD Review
- Active Ingredient: Copper
- Release Form: Intrauterine Device
- Age: 25 - 65 years
- Average Price: $500 - $800

ParaGard Review
- Active Ingredient: Copper
- Release Form: Intrauterine Device
- Age: 25 - 65 years
- Average Price: $500 - $739
Kyleena Review
- Active Ingredient: Levonorgestrel
- Release Form: Intrauterine Device
- Age: 25 - 65 years
- Average Price: $500 - $900
Skyla Review
- Active Ingredient: Levonorgestrel
- Release Form: Intrauterine Device
- Age: 25 - 65 years
- Average Price: $650 - $780
Liletta Review
- Active Ingredient: Levonorgestrel
- Release Form: Intrauterine Device
- Age: 16 - 45 years
- Average Price: $720
Vaginal ring
The vaginal ring is a combined hormonal birth control. Its action is aimed at suppressing the ovulation process. The contraceptive is released in the form of an elastic transparent ring made of hypoallergenic material (latex). Product dimensions are standard: about 4 mm*54 mm. The contraceptive ring is fit for women of any body constitution.
It takes a shape that matches the vaginal anatomical structure. A correctly placed contraceptive does not cause discomfort. A woman can continue her usual work activity, engage in her favorite types of physical activity. During intimacy, partners do not experience any inconvenience.
Mode of operation
In the gynecological practice, contraceptive vaginal rings have been used for about ten years. It contains two female hormones: progestogen and estrogen. These active substances effectively block the ovulation. It also prevent the penetration of sperm, increasing the density of cervical mucus.
It takes several days for the hormonal contraceptive to start acting. Being in the vagina and warming up to body temperature, the vaginal ring begins to release hormones in microdoses. Their rate is significantly less than in any hormonal contraceptive pill. Only the ovaries and uterus are affected by hormones.

Annovera Review
- Active Ingredient: Segesterone Acetate / Ethinyl Estradiol
- Release Form: Vaginal Ring
- Age: 18 - 40 years
- Average Price: $1981.20
Nexplanon Review
Etonogestrel Implant Review
Implanon Review